Table of Contents
Introduction
Foot health is an essential aspect of overall well-being that is often overlooked. The foot, a complex structure with 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments, plays a crucial role in our daily activities such as walking, running, and jumping. Among these components, the arch of the foot, which serves as the body’s natural shock absorber, is particularly important. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of pain in the arch of the foot can help you maintain your foot health and continue your daily activities without discomfort.
The arch of the foot, a curved structure formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, is strengthened by tendons and ligaments. It helps distribute body weight across the feet and legs, ensuring that not all the pressure falls on one part of the foot. The arch’s health and integrity are crucial for foot function, and any issues with it can lead to pain and other complications.
Pain in the arch of the foot can be a significant hindrance, affecting mobility and quality of life. It can be caused by various factors, including injury, overuse, or conditions like plantar fasciitis or flat feet. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding pain in the arch of the foot, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, and preventive measures to maintain foot health.
Understanding the Foot and Its Arch
The foot, a marvel of biological engineering, is designed to withstand the pressures of daily activities and provide a firm foundation for the body. It’s a complex structure, composed of numerous bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working together to provide balance, stability, and mobility.
Anatomy of the Foot
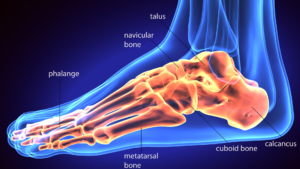 The foot is divided into three sections: the forefoot, the midfoot, and the hindfoot. The forefoot includes the five toes (phalanges) and their connecting long bones (metatarsals). The midfoot, also known as the arch, comprises the pyramid-like tarsal bones. The hindfoot connects the midfoot and the ankle (talus) and heel (calcaneus) bones.
The foot is divided into three sections: the forefoot, the midfoot, and the hindfoot. The forefoot includes the five toes (phalanges) and their connecting long bones (metatarsals). The midfoot, also known as the arch, comprises the pyramid-like tarsal bones. The hindfoot connects the midfoot and the ankle (talus) and heel (calcaneus) bones.
The arch of the foot, the focus of our discussion, is a curved region located along the bottom of the foot, between the heel and the forefoot. It’s formed by five tarsal bones, with the primary ones being the talus, calcaneus, navicular, and three cuneiform bones. These bones are connected by a series of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, creating a robust, flexible structure that absorbs shock and adapts to various surfaces.
There are two main arches in the foot: the longitudinal arch, which runs lengthwise along the foot, and the transverse arch, which runs widthwise. The longitudinal arch can be further divided into the medial arch (the high arch on the inside of the foot) and the lateral arch (the low arch on the outside of the foot).
The Role of the Arch in Foot Health
The arches of the foot play a crucial role in how we move. They act as natural shock absorbers, cushioning the impact on the rest of the body during physical activities such as walking, running, or jumping. The arches also help distribute body weight evenly across the feet and provide a spring to our step, aiding in propulsion.
When the foot lands on the ground, the arches flex to absorb the impact, reducing the shock that could otherwise jolt up through the legs and spine. When the foot lifts off the ground, the arches spring back, helping to propel the body forward.
Problems with the arch can lead to pain and other complications. For instance, if the arches are too high, they may not absorb shock effectively, leading to potential joint and muscle pain. On the other hand, if the arches are too low or flat, they may not provide enough support, which can lead to foot, knee, hip, and back problems.

Causes of Pain in the Arch of Foot
Pain in the arch of the foot can be caused by various factors, ranging from structural abnormalities and injuries to lifestyle factors and certain health conditions. Understanding these causes can help in the diagnosis and treatment of arch pain.
Common Causes
One of the most common causes of arch pain is plantar fasciitis. This condition occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel to the toes and supports the arch of the foot, becomes inflamed. This inflammation can cause a stabbing pain in the arch of the foot, especially with the first steps in the morning or after long periods of standing or sitting.
Flat feet, also known as fallen arches, is another common cause of arch pain. This condition occurs when the arches of the feet collapse, either partially or completely, causing the entire soles of the feet to touch the floor when standing. Flat feet can be congenital (present at birth) or can develop over time due to aging, obesity, or injury. The lack of proper arch support can lead to foot pain, including in the arch.
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a condition that can cause arch pain. The posterior tibial tendon, which runs from the calf, around the inside of the ankle, and attaches to the middle of the arch, can become inflamed or torn. If this tendon is damaged, it can lead to flat feet and pain in the arch.
Other conditions that can cause arch pain include cavus foot (high arches), tarsal tunnel syndrome, and arthritis. Injuries, such as sprains or fractures, can also lead to arch pain.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to arch pain. For instance, physical activities that put a lot of stress on the feet, such as running or jumping, can lead to overuse injuries causing arch pain. Similarly, occupations that require long periods of standing or walking can put excessive pressure on the arch, leading to pain.
Footwear can also play a significant role in arch pain. Shoes that do not provide proper arch support or that are too tight can contribute to foot pain. High heels, in particular, can put a lot of stress on the arch and lead to pain.
Understanding these causes can help in the prevention and treatment of arch pain. In the next sections, we will explore the symptoms and diagnosis of arch pain, as well as treatment options and prevention strategies.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Pain in the Arch of Foot
Recognizing the symptoms of arch pain and seeking timely medical attention is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further complications. The diagnostic process involves a thorough examination and may include various tests to determine the underlying cause of the pain.
Recognizing the Symptoms
 The primary symptom of arch pain is, unsurprisingly, pain in the arch of the foot. However, the nature of the pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. It may be described as a sharp, burning, or throbbing pain. The pain may be constant, or it may come and go. It may be worse in the morning, after standing or walking for long periods, or during certain activities.
The primary symptom of arch pain is, unsurprisingly, pain in the arch of the foot. However, the nature of the pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. It may be described as a sharp, burning, or throbbing pain. The pain may be constant, or it may come and go. It may be worse in the morning, after standing or walking for long periods, or during certain activities.
In addition to pain, other symptoms may include:
- Swelling in the arch of the foot
- Redness and warmth over the arch
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Pain that increases with activity and decreases with rest
- Flat feet or high arches
If you experience persistent pain in the arch of your foot, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and causing further complications.
The Diagnostic Process
 The diagnosis of arch pain begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, their onset and duration, any previous foot injuries or conditions, your physical activities, and the type of footwear you use.
The diagnosis of arch pain begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, their onset and duration, any previous foot injuries or conditions, your physical activities, and the type of footwear you use.
During the physical examination, your doctor will examine your foot for signs of inflammation, such as redness, warmth, and swelling. They may ask you to walk or perform certain movements to assess your foot’s function and determine when the pain occurs.
In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. These tests may include:
- X-rays: These can provide images of the bones in the foot and can help identify abnormalities such as fractures or arthritis.
- MRI or ultrasound: These imaging tests can provide detailed images of the soft tissues in the foot, including muscles, ligaments, and tendons. They can help identify conditions such as plantar fasciitis or tendon tears.
- Blood tests: If your doctor suspects a systemic disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, they may order blood tests.
Once the cause of the arch pain is identified, your doctor can develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. In the following sections, we will explore the various treatment options for arch pain, as well as strategies for prevention.
Treatment Options for Pain in the Arch of Foot
The treatment for pain in the arch of the foot largely depends on the underlying cause. It typically involves a combination of home remedies, physical therapy exercises, and in some cases, medical treatments. The goal of treatment is to relieve pain, improve foot function, and prevent further complications.
Home Remedies and Exercises
For many people, home remedies and exercises can effectively manage arch pain. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Rest and Ice: If your arch pain is due to overuse or strain, rest can help your foot recover. Avoid activities that cause pain, such as running or jumping. Applying ice to the painful area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Foot Exercises: Certain exercises can help strengthen the muscles in your feet, improve flexibility, and support your arches. These may include toe curls, heel raises, and towel stretches. A physical therapist can provide a personalized exercise program based on your specific needs.
- Over-the-counter Pain Relievers: Non-prescription medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Arch Supports: Over-the-counter arch supports or custom orthotics can provide additional support to your arches, distribute pressure evenly across your feet, and alleviate pain.
Medical Treatments
 If home remedies and exercises are not enough, medical treatments may be necessary. These can include:
If home remedies and exercises are not enough, medical treatments may be necessary. These can include:
- Prescription Medication: Your doctor may prescribe stronger pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications if over-the-counter drugs are not effective. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce severe inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide a personalized exercise program to improve the strength and flexibility of your foot muscles. They may also use other treatments such as ultrasound therapy or massage.
- Orthotics: If over-the-counter arch supports are not helpful, custom-made orthotics may be recommended. These are designed to fit your feet precisely and provide the right amount of arch support.
- Surgery: In rare cases, if the arch pain is due to a structural problem in the foot or if other treatments have not been effective, surgery may be necessary.
It’s important to remember that treatment can take time, and it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s advice and treatment plan.
Prevention Strategies for Pain in the Arch of Foot
Preventing arch pain is often a matter of taking care of your feet and making wise lifestyle choices. Here are some strategies that can help prevent arch pain and maintain foot health:
Footwear and Foot Care
The shoes you wear can have a significant impact on your foot health. Here are some tips for choosing the right footwear:
- Choose the right size: Shoes that are too small or too tight can squeeze your feet and cause pain, while shoes that are too large can cause your feet to slide and create friction. Make sure your shoes are the right size for your feet.
- Look for good arch support: Shoes with good arch support can help prevent flat feet and alleviate the pressure on your arches. If necessary, consider using over-the-counter arch supports or custom orthotics.
- Avoid high heels: High heels can put a lot of pressure on the front of your feet and your arches. If you must wear heels, choose lower, more stable heels and limit the time you wear them.
- Change your shoes regularly: Over time, shoes lose their cushioning and support. Changing your shoes regularly can ensure that your feet are always well-supported.
In addition to choosing the right footwear, proper foot care is also essential. This includes keeping your feet clean and dry, trimming your toenails regularly, and checking your feet for any signs of problems such as cuts, blisters, or infections.
Lifestyle Modifications
 Certain lifestyle modifications can also help prevent arch pain:
Certain lifestyle modifications can also help prevent arch pain:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Carrying extra weight can put more pressure on your feet and your arches. Maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent foot problems.
- Stay active: Regular physical activity can help keep your feet strong and healthy. Choose activities that you enjoy and that are appropriate for your fitness level.
- Stretch regularly: Regular stretching can help improve the flexibility of your feet and reduce the risk of injuries. Consider including foot stretches in your daily routine.
- Take breaks: If your job involves standing or walking for long periods, make sure to take regular breaks to rest your feet.
By following these prevention strategies, you can help keep your feet healthy and prevent arch pain.
Living with Pain in the Arch of Foot
Living with pain in the arch of the foot can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it’s possible to manage the pain and maintain a good quality of life. Here are some tips for managing foot arch pain in daily life and improving overall foot health:
Managing Pain in Daily Life
 Follow your treatment plan: Once your doctor has diagnosed the cause of your arch pain and developed a treatment plan, it’s crucial to follow it. This may include taking prescribed medications, doing recommended exercises, and using orthotics or other supportive devices.
Follow your treatment plan: Once your doctor has diagnosed the cause of your arch pain and developed a treatment plan, it’s crucial to follow it. This may include taking prescribed medications, doing recommended exercises, and using orthotics or other supportive devices.- Modify your activities: If certain activities exacerbate your arch pain, try to modify them or find alternatives. For example, if running causes pain, you might switch to lower-impact activities like swimming or cycling.
- Use pain management techniques: In addition to medication, other techniques can help manage pain. These might include relaxation techniques, heat or cold therapy, or over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Keep up with regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your foot doctor or podiatrist can help monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Improving Foot Health
- Choose footwear wisely: As mentioned earlier, the right footwear can make a significant difference in managing and preventing arch pain. Choose shoes with good arch support, a roomy toe box, and a comfortable fit.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Extra weight can put additional stress on your feet, contributing to arch pain. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate this pressure.
- Exercise your feet: Just like any other part of your body, your feet can benefit from regular exercise. Simple foot and ankle exercises can help strengthen your feet, improve flexibility, and support your arches.
- Take care of your feet: Regular foot care, including washing your feet daily, moisturizing them, and checking for any changes or abnormalities, can help prevent foot problems.
Living with arch pain can be challenging, but with the right strategies and care, you can manage the pain and maintain an active, healthy lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer some frequently asked questions about pain in the arch of the foot. These answers provide a quick reference to some of the key points discussed in this article.
What causes pain in the arch of the foot?
Pain in the arch of the foot can be caused by various factors, including structural abnormalities, injuries, certain health conditions, and lifestyle factors. Common causes include plantar fasciitis, flat feet, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, and overuse or strain from physical activities or improper footwear.
How is pain in the arch of the foot diagnosed?
The diagnosis of arch pain begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your doctor may ask about your symptoms, their onset and duration, any previous foot injuries or conditions, your physical activities, and the type of footwear you use. In some cases, further diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRI, or blood tests may be required.
What are the treatment options for pain in the arch of the foot?
Treatment for arch pain depends on the underlying cause. It typically involves a combination of home remedies, physical therapy exercises, and in some cases, medical treatments. Home remedies and exercises can include rest, ice, foot exercises, over-the-counter pain relievers, and arch supports. Medical treatments can include prescription medication, physical therapy, custom orthotics, and in rare cases, surgery.
How can pain in the arch of the foot be prevented?
Preventing arch pain often involves taking care of your feet and making wise lifestyle choices. This includes choosing the right footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, stretching regularly, and taking breaks if your job involves standing or walking for long periods.
What exercises can help with pain in the arch of the foot?
Certain exercises can help strengthen the muscles in your feet, improve flexibility, and support your arches. These may include toe curls, heel raises, and towel stretches. A physical therapist can provide a personalized exercise program based on your specific needs.
When should I see a doctor for pain in the arch of the foot?
If you experience persistent pain in the arch of your foot, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and causing further complications.
Can shoes cause pain in the arch of the foot?
Yes, improper footwear can contribute to arch pain. Shoes that do not provide proper arch support or that are too tight can contribute to foot pain. High heels, in particular, can put a lot of stress on the arch and lead to pain.
How long does it take for pain in the arch of the foot to heal?
The healing time for arch pain depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. With proper treatment, most cases of arch pain improve within a few weeks. However, some conditions may take longer to heal, and chronic conditions may require ongoing management.
Can pain in the arch of the foot be a sign of a more serious condition?
While most cases of arch pain are due to common foot conditions or injuries, in some cases, it can be a sign of a more serious condition such as arthritis or a nerve disorder. If you have persistent arch pain, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
What lifestyle changes can help manage pain in the arch of the foot?
Lifestyle changes that can help manage arch pain include maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, choosing the right footwear, taking breaks if your job involves standing or walking for long periods, and taking care of your feet. Regular foot exercises can also help strengthen your feet and support your arches.
Additional Information
In this section, we delve into specific types of arch pain, providing more detailed information to help you understand and manage these conditions.
Pain in arch of foot when walking
This type of pain can be caused by plantar fasciitis, flat feet, or other foot conditions. It can also be exacerbated by improper footwear or overuse. Walking, especially for long distances or on hard surfaces, can put extra stress on the arch, leading to pain.
Sharp pain in arch of foot
Sharp pain in the arch of the foot can be a sign of a strain or sprain in the muscles or ligaments that support the arch. It can also be a symptom of plantar fasciitis, a condition that causes inflammation in the band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot.
Throbbing pain in arch of foot
Throbbing pain in the arch of the foot can be a sign of an injury or inflammation. It can also be a symptom of a more serious condition such as a fracture or a nerve problem. If you experience throbbing pain in your arch, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Burning pain in arch of foot
Burning pain in the arch of the foot can be caused by nerve damage or a condition called tarsal tunnel syndrome, which is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome but affects the nerves in the foot instead of the wrist. It can also be a symptom of neuropathy, a condition that affects the nerves in the feet and is often associated with diabetes.
Stabbing pain in arch of foot
Stabbing pain in the arch of the foot can be a sign of plantar fasciitis or another foot condition. It can also be caused by a sharp object penetrating the foot, although this is less common.
Pain in arch of foot when resting
Pain in the arch of the foot when resting can be a sign of a chronic foot condition such as plantar fasciitis or tarsal tunnel syndrome. It can also be caused by resting the foot in an awkward position that puts stress on the arch.
Pain in arch of foot after running
Running puts a lot of stress on the feet, and it’s common to experience foot pain after running, especially if you have flat feet or high arches. Overuse, improper running technique, or running in shoes that don’t provide adequate support can also lead to arch pain.
Pain in arch of foot during pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause changes in the body that lead to foot pain. The extra weight of pregnancy can put more stress on the feet, and hormonal changes can loosen the ligaments in the feet, both of which can lead to arch pain.
Pain in arch of foot from high arches
High arches can put extra stress on the metatarsals, the bones in the middle of the foot, leading to pain. High arches can also lead to other foot problems such as metatarsalgia, a painful inflammation in the ball of the foot.
Pain in arch of foot from flat feet
Flat feet, or fallen arches, can lead to foot pain, particularly in the arch or heel area. The pain can worsen with activity or prolonged standing.
Conclusion
Foot health is an essential aspect of overall well-being that often gets overlooked. The arch of the foot, in particular, plays a crucial role in our daily activities, from walking and running to standing and balancing. Pain in the arch of the foot can significantly affect our mobility and quality of life.
Understanding the causes of arch pain is the first step towards effective treatment. Common causes include structural abnormalities such as flat feet or high arches, injuries, overuse, and certain health conditions. Lifestyle factors such as physical activity and footwear can also contribute to arch pain.
Recognizing the symptoms of arch pain and seeking timely medical attention is crucial. Symptoms can include pain in the arch of the foot when walking, sharp or throbbing pain, burning or stabbing sensations, or pain when resting. If you experience persistent or severe foot pain, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
Treatment for arch pain typically involves a combination of home remedies, exercises, and medical treatments. Home remedies and exercises can help alleviate pain, improve foot strength and flexibility, and support the arches. Medical treatments can include orthotics, medication, and in rare cases, surgery.
Prevention strategies for arch pain include choosing the right footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and taking care of your feet. Regular foot exercises can help strengthen your feet and support your arches. If your job involves standing or walking for long periods, taking breaks and not overexerting your feet can help prevent arch pain.
Living with arch pain can be challenging, but with the right management strategies, it’s possible to lead a normal, active life. Following your treatment plan, regular check-ups, and making wise lifestyle choices can help manage arch pain and improve your foot health.
In conclusion, taking care of your foot health is an investment in your overall health and well-being. Whether you’re dealing with arch pain or other foot problems, remember that help is available, and it’s never too late to start taking better care of your feet


 Follow your treatment plan: Once your doctor has diagnosed the cause of your arch pain and developed a treatment plan, it’s crucial to follow it. This may include taking prescribed medications, doing recommended exercises, and using orthotics or other supportive devices.
Follow your treatment plan: Once your doctor has diagnosed the cause of your arch pain and developed a treatment plan, it’s crucial to follow it. This may include taking prescribed medications, doing recommended exercises, and using orthotics or other supportive devices.


