Metatarsal Fractures: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Metatarsal fractures, a common injury among athletes and non-athletes alike, can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. These fractures occur in the long bones of the foot and can range from minor cracks to complete breaks. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options is crucial for effective recovery and prevention of future injuries.
Whether you’re dealing with a recent injury or seeking to prevent one, this article will provide you with the knowledge you need to take care of your feet and stay active.
Table of Contents
What is a Metatarsal Fracture?
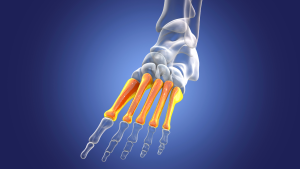 The human foot consists of five metatarsal bones, which stretch from the ankle to the toes. These bones play a pivotal role in how we walk and balance. A metatarsal fracture occurs when one or more of these bones break. The fractures can be categorized into two main types: acute fractures, which result from direct trauma or injury, and stress fractures, which develop over time due to repeated stress.
The human foot consists of five metatarsal bones, which stretch from the ankle to the toes. These bones play a pivotal role in how we walk and balance. A metatarsal fracture occurs when one or more of these bones break. The fractures can be categorized into two main types: acute fractures, which result from direct trauma or injury, and stress fractures, which develop over time due to repeated stress.
What Causes a Foot Metatarsal Fracture?
Metatarsal fractures stem from a variety of causes, each linked to different activities and risk factors. One common cause is direct impact or trauma, such as dropping a heavy object on the foot or experiencing a fall. Sports-related injuries are also frequent culprits, particularly in sports that involve running, jumping, or sudden changes in direction.
Another significant cause of metatarsal fractures is overuse, leading to stress fractures. These are especially prevalent among athletes, dancers, and military recruits who engage in rigorous training routines. Continuous stress on the foot without adequate rest breaks down the bone over time, eventually leading to a fracture.
Certain lifestyle factors can also increase the risk of metatarsal fractures. Poor footwear, such as shoes that lack proper support or cushioning, can contribute to the likelihood of injury. Additionally, individuals with osteoporosis or other conditions that weaken bones are at higher risk.

Identifying Symptoms of Metatarsal Fracture and Stress Fracture Swelling
 Recognizing the symptoms of a metatarsal fracture early can greatly improve the outcome. The most common symptom is pain at the site of the fracture, which may worsen with activity and improve with rest. This pain often starts out as mild and increases with continued pressure on the foot.
Recognizing the symptoms of a metatarsal fracture early can greatly improve the outcome. The most common symptom is pain at the site of the fracture, which may worsen with activity and improve with rest. This pain often starts out as mild and increases with continued pressure on the foot.
Swelling is another key indicator of a metatarsal fracture. The top of the foot may appear visibly swollen and feel tender to the touch. Bruising can also occur, displaying a range of colors from dark purple to yellow around the affected area.
In cases of stress fractures, the symptoms develop gradually and may be less obvious. Sufferers might experience aching or throbbing pain during or after physical activity, which initially subsides with rest but becomes more persistent as the injury worsens.
If you suspect a metatarsal fracture, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation. Ignoring these signs can lead to more severe complications, including shifts in bone alignment and prolonged healing times. Early detection and treatment are key to a swift recovery.
Diagnosing Metatarsal Fractures
Diagnosing a metatarsal fracture accurately is crucial for effective treatment. The first step is usually a detailed patient history and physical examination. A podiatrist or doctor will ask about any recent injuries or activities and check the foot for signs of swelling, bruising, and tenderness.
Imaging tests play a vital role in confirming the diagnosis. An X-ray is the most common tool used to visualize the extent of the fracture. In some cases, if the X-ray does not show clear results but a fracture is still suspected, additional imaging such as MRI or CT scan may be recommended.
These tests help to identify not just the presence of a fracture but also its type, location, and severity. This information is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. It allows healthcare providers to determine whether a conservative approach like rest and immobilization is sufficient, or if surgical intervention is needed.
Treatment Options for Metatarsal Fractures
 Treatment for metatarsal fractures varies depending on the type and severity of the fracture. For less severe fractures, immobilization is often the first step. This may involve wearing a cast, boot, or stiff-soled shoe to keep the foot stable and relieve pressure, allowing the bone to heal.
Treatment for metatarsal fractures varies depending on the type and severity of the fracture. For less severe fractures, immobilization is often the first step. This may involve wearing a cast, boot, or stiff-soled shoe to keep the foot stable and relieve pressure, allowing the bone to heal.
For stress fractures, treatment usually includes rest and reducing activities that put stress on the foot. Ice and elevation can help reduce swelling and pain. Physical therapy may also be recommended to strengthen the foot and improve flexibility once the bone starts to heal.
When conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief or when the fracture is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary for metatarsal fractures. Surgical options typically involve the use of internal fixation devices such as screws, plates, or pins to stabilize the broken bone and ensure proper alignment during the healing process. The choice of surgical method depends on the location and complexity of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health and activity level. Post-surgery, patients may require physical therapy to restore strength and mobility in the foot. While surgery can effectively mend the fracture and expedite recovery, it also carries risks such as infection, nerve damage, and prolonged rehabilitation. Therefore, a thorough discussion with a foot surgeon is essential to weigh the benefits and potential complications of surgical treatment for metatarsal fractures.
Surgical Options for Metatarsal Fractures
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF):
- Description: Involves surgically exposing the fracture site and using screws, plates, or pins to secure the bones in proper alignment.
- Indications: Typically used for severe fractures with significant displacement or when multiple metatarsals are fractured.
Percutaneous Fixation:
- Description: Minimally invasive procedure where pins or screws are inserted through small incisions to stabilize the fracture.
- Indications: Suitable for less complex fractures where the bones are not severely displaced.
Intramedullary Fixation:
- Description: Involves inserting a rod or nail into the marrow canal of the metatarsal bone to maintain alignment.
- Indications: Often used for fractures of the metatarsal shaft, particularly in cases where other methods are not feasible.
External Fixation:
- Description: A frame is placed outside the foot with pins inserted into the bone to hold the fracture in place.
- Indications: Used for complex fractures, open fractures, or when there is significant soft tissue damage that precludes internal fixation.
Bone Grafting:
- Description: In cases where there is bone loss or a non-union, bone grafting may be performed to promote healing.
- Indications: Often used in conjunction with other fixation methods for severe or non-healing fractures.
Each surgical option has its own set of advantages and potential risks, and the choice of procedure depends on the specific circumstances of the fracture and the patient’s overall health. Consulting with a foot surgeon will help determine the most appropriate surgical intervention.
Conclusion
Recognizing and treating metatarsal fractures promptly is essential for a swift recovery and return to daily activities. These injuries, while common, vary greatly in terms of impact and treatment approaches. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps toward healing. Always consult a podiatrist or foot surgeon if you suspect a fracture, as they can provide the necessary guidance and care. Remember, taking care of your foot health is a step towards maintaining your overall well-being and mobility. Stay informed, stay safe, and ensure you follow through with treatment plans to achieve the best recovery possible.
Get Expert Metatarsal Fracture Treatment
 Don’t let foot pain slow you down! If you suspect a metatarsal fracture or have foot concerns, it’s important to act swiftly. Schedule an appointment with Ankle & Foot Centers of America, where our specialists are dedicated to helping you get back on your feet. Call us today at 404-508-4026 to find a location near you and ensure the best care for your foot health. Your journey to recovery starts with the right care—let us help you take the first step.
Don’t let foot pain slow you down! If you suspect a metatarsal fracture or have foot concerns, it’s important to act swiftly. Schedule an appointment with Ankle & Foot Centers of America, where our specialists are dedicated to helping you get back on your feet. Call us today at 404-508-4026 to find a location near you and ensure the best care for your foot health. Your journey to recovery starts with the right care—let us help you take the first step.
About Dr. Joshua Wilder
Dr. Joshua Wilder, a distinguished podiatrist and foot surgeon, brings extensive experience to the table in treating foot and ankle conditions. Having completed his undergraduate studies at Washington and Jefferson College, Dr. Wilder earned his medical degree from Kent State University College of Podiatric Medicine. His postgraduate training included a focus on rearfoot reconstruction and limb salvage, complemented by a fellowship in pediatric and adult reconstructive foot and ankle surgery. Dr. Wilder’s affiliation with several prestigious medical organizations and hospitals underscores his commitment to advancing foot and ankle care.






