Table of Contents
Introduction
Foot reconstruction surgery represents a beacon of hope for those suffering from foot deformities and chronic pain. It’s not just a medical procedure; it’s a pathway to improved mobility, comfort, and overall quality of life. In this article, we’ll discuss foot reconstruction surgery, including flat foot reconstruction surgery and Charcot foot reconstruction surgery, and other types of reconstructive foot surgery. Our goal is to provide you with a thorough understanding of these procedures, helping you make informed decisions about your foot health.
Understanding Foot Reconstruction Surgery
Foot reconstruction surgery encompasses a range of surgical procedures aimed at correcting deformities and restoring function to the foot. Whether due to injury, disease, or congenital conditions, these surgeries can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.
Definition and Purpose
Reconstructive foot surgery is a specialized field of orthopedic surgery focused on correcting deformities and dysfunctions of the foot. The primary goal is to restore normal function, alleviate pain, and improve the appearance of the foot. These procedures range from minor bunion corrections to complex reconstructions for severe deformities.

Common Conditions Leading to Surgery
Several conditions may necessitate foot reconstruction surgery. Flat feet, a condition where the arches of the feet are flattened, can lead to pain and mobility issues. Charcot foot, a severe complication often associated with diabetes, involves weakening of the bones in the foot, leading to fractures and dislocations. Other conditions include severe bunions, hammertoes, and injuries that have led to misalignment or loss of function.
Improving Quality of Life
The impact of foot reconstruction surgery on a patient’s life can be profound. By addressing the root cause of foot pain and deformity, these surgeries can lead to significant improvements in walking ability, comfort, and overall foot function. This, in turn, enhances the patient’s ability to engage in daily activities and enjoy a more active lifestyle, free from the constraints of chronic foot pain.
Flat Foot Reconstruction Surgery
 Flat foot, or pes planus, is a condition where the arch of the foot collapses, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. While some individuals with flat feet experience no issues, others may suffer from pain and mobility problems. Flat foot reconstruction surgery aims to alleviate these symptoms by restoring the natural arch of the foot.
Flat foot, or pes planus, is a condition where the arch of the foot collapses, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. While some individuals with flat feet experience no issues, others may suffer from pain and mobility problems. Flat foot reconstruction surgery aims to alleviate these symptoms by restoring the natural arch of the foot.
What are Flat Feet?
Flat feet can be a congenital condition, meaning some people are born with it, or it can develop over time due to age, injury, or wear and tear. Symptoms often include pain in the foot, particularly in the arch and heel, swelling along the inside of the ankle, and a general feeling of fatigue in the feet or legs.
Indications for Surgery
Surgery is considered when conservative treatments, such as orthotics, physical therapy, and pain relief medications, have failed to alleviate the symptoms. Candidates for flat foot reconstruction are typically those experiencing significant discomfort, limited function, and a decreased quality of life due to the condition.
Surgical Procedures Overview
The surgical approach to flat foot reconstruction varies depending on the severity of the condition and the specific needs of the patient. Common procedures include:
- Osteotomy: Cutting and realigning bones to correct deformities.
- Tendon Transfer: Repositioning tendons to provide better support for the arch.
- Arthrodesis: Fusing bones together to stabilize the foot and ankle.
- Ligament Repair: Tightening or repairing ligaments to provide better arch support.
Each of these procedures aims to improve alignment, reduce pain, and enhance functionality.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from flat foot reconstruction surgery can be a lengthy process, often taking several months. Initially, patients may need to wear a cast or boot and use crutches to keep weight off the foot. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in recovery, helping to restore strength and mobility. Most patients can expect a gradual return to normal activities, although complete healing and maximum improvement may take up to a year.
Charcot Foot Reconstruction Surgery
 Charcot foot is a serious condition often associated with diabetes and neuropathy, where the bones in the foot weaken and can fracture, leading to significant deformities. Charcot foot reconstruction surgery is a complex procedure aimed at stabilizing the foot, correcting deformities, and preventing further deterioration.
Charcot foot is a serious condition often associated with diabetes and neuropathy, where the bones in the foot weaken and can fracture, leading to significant deformities. Charcot foot reconstruction surgery is a complex procedure aimed at stabilizing the foot, correcting deformities, and preventing further deterioration.
Understanding Charcot Foot
Charcot foot develops as a result of nerve damage (neuropathy) which diminishes the ability to sense trauma or pressure on the foot. As a result, bones can fracture or dislocate without the individual realizing it, leading to progressive deformities. The condition is most commonly associated with diabetes but can result from other causes of neuropathy as well.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of Charcot foot are crucial. In its early stages, the condition can often be managed non-surgically, such as with immobilization or custom footwear. However, if left untreated, it can lead to severe deformities, ulcers, and even the need for amputation.
Surgical Options
 When surgery is required, the specific procedures depend on the severity and location of the deformity. Common surgical interventions include:
When surgery is required, the specific procedures depend on the severity and location of the deformity. Common surgical interventions include:
- Osteotomy: To remove bony prominences and correct deformities.
- Arthrodesis: Fusing bones to provide stability and correct misalignment.
- Bone Grafting: To help in healing and reconstruction in cases of bone loss.
- External Fixation: Using external frames to hold bones in the correct position as they heal.
These procedures aim to create a stable, functional foot that can bear weight without causing ulcers or pain.
Post-Operative Care
Recovery from Charcot foot reconstruction surgery is typically lengthy and requires careful management. Patients will likely need to wear a cast or specialized boot for several weeks or months and avoid putting weight on the foot. Physical therapy is essential for regaining strength and mobility. The overall goal of post-operative care is to ensure proper healing and prevent recurrence of the condition.
The Surgical Process
Understanding the surgical process for foot reconstruction surgery is crucial for patients preparing for the procedure. This section outlines the typical steps involved, from pre-surgical evaluations to the surgery itself and immediate post-operative care.
Pre-Surgical Evaluations
Before undergoing foot reconstruction surgery, several preparatory steps are necessary:
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical examination to assess overall health and identify any conditions that could affect surgery or recovery.
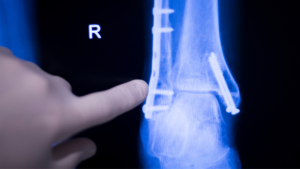
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to determine the extent of the deformity and plan the surgical approach.
- Consultation with the Surgeon: Discussing the surgical options, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
- Pre-Operative Instructions: Guidelines on medication, fasting, and other preparations before the surgery.
Step-by-Step Guide to Surgery
The specific steps of foot reconstruction surgery vary based on the type of procedure being performed, but generally include:
- Anesthesia: Administration of general or regional anesthesia to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the operation.
- Incision: Making strategic cuts to access the bones, joints, and ligaments needing correction.
- Correction Procedure: Depending on the condition, this may involve realigning bones, repairing or transferring tendons, or fusing joints.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or staples.
- Bandaging: The foot is bandaged, and often a cast or boot is applied to immobilize the foot during the initial healing phase.
Anesthesia and Pain Management
Anesthesia options may include general anesthesia (where the patient is completely asleep) or regional anesthesia (numbing only a portion of the body). Post-operative pain management is a critical aspect of care, often involving medications, ice, elevation, and rest to control swelling and discomfort.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Immediately following surgery, patients are typically taken to a recovery room where they are closely monitored as the anesthesia wears off. Key aspects of immediate post-operative care include:
- Pain Management: Administering pain relief medications as needed.
- Monitoring for Complications: Watching for any signs of infection, bleeding, or other complications.
- Initial Mobility: Guidance on when and how to move or bear weight on the operated foot.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, foot reconstruction surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. It’s important for patients to be aware of these to make informed decisions and to recognize symptoms if they occur post-surgery.
Common Risks
Some of the common risks associated with foot reconstruction surgery include:
- Infection: Although rare, infections can occur at the site of the surgery and may require antibiotics or additional surgery.
- Blood Clots: Surgery can increase the risk of blood clots, especially in the legs. Preventative measures may include blood thinners or compression devices.
- Nerve Damage: There’s a risk of nerve damage during surgery, which can lead to numbness or tingling.
- Anesthesia Risks: Reactions to anesthesia, though uncommon, can include respiratory issues or allergic reactions.
Minimizing Complications
To minimize the risk of complications, patients should:
- Follow Pre- and Post-Operative Instructions: Adhering to the surgeon’s guidelines can significantly reduce risks.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Proper care of the surgical site is crucial to prevent infection.
- Stay Active as Recommended: Gentle movements or exercises as advised by the healthcare provider can help prevent blood clots and aid in recovery.
- Report Any Concerns: Promptly reporting signs of infection, unusual pain, or changes in sensation can allow for early intervention.
Post-Surgery Red Flags
Patients should be vigilant for symptoms that might indicate a complication, such as:
- Increased Pain or Swelling: While some pain and swelling are normal, a sudden increase can be a warning sign.
- Redness, Heat, or Drainage at the Surgical Site: These can be signs of infection.
- Shortness of Breath or Chest Pain: These symptoms could indicate a blood clot and require immediate medical attention.
Long-Term Complications
In some cases, long-term issues may arise, such as:
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort: Some patients may continue to experience pain or discomfort in the foot.
- Limited Mobility or Flexibility: Despite successful surgery, some degree of limitation may remain, depending on the severity of the pre-surgical condition.
Understanding these risks and how to manage them is a key part of preparing for foot reconstruction surgery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery and rehabilitation are critical components of the journey after foot reconstruction surgery. This phase is essential for ensuring the best possible outcome and for returning to normal activities safely and effectively.
Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline can vary greatly depending on the type of surgery performed and the individual patient. Generally, it can be broken down into several stages:
- Immediate Post-Operative Period (First Few Weeks): During this time, patients often wear a cast or boot and are advised to limit weight-bearing on the affected foot. Pain management and wound care are crucial.
- Intermediate Recovery (1-3 Months): As healing progresses, patients may start gentle physical therapy exercises to improve strength and flexibility. Gradual weight-bearing is often introduced during this phase.
- Late Recovery (3-6 Months and Beyond): Full recovery can take several months. During this period, patients typically work on regaining full strength, mobility, and function in the foot.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy plays a vital role in recovery. A physical therapist will guide patients through exercises designed to:
- Restore Strength: Building up the muscles in the foot and leg.
- Improve Flexibility: Stretching exercises to maintain or improve the range of motion.
- Enhance Mobility: Gradually returning to walking and other activities.
It’s important to follow the therapist’s instructions and not rush the process, as doing too much too soon can hinder recovery.
Lifestyle Changes for Recovery
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can aid in a smoother and quicker recovery:
- Elevating the Foot: To reduce swelling, it’s often recommended to keep the foot elevated above heart level, especially in the first few weeks after surgery.
- Diet and Nutrition: A healthy diet can promote healing. Some patients may be advised to increase their intake of certain nutrients like protein and calcium.
- Footwear Modifications: Wearing supportive, comfortable shoes is important post-recovery. In some cases, custom orthotics may be recommended.
Long-Term Care and Maintenance
Even after full recovery, it’s important to continue caring for the reconstructed foot:
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine visits to the surgeon or podiatrist can help monitor the long-term success of the surgery.
- Continued Exercise and Activity: Staying active and maintaining foot strength and flexibility can help prevent future issues.
Conclusion
Foot reconstruction surgery, encompassing procedures like flat foot reconstruction and Charcot foot reconstruction, is a significant step towards resolving foot deformities and improving quality of life. This comprehensive guide has walked you through the various aspects of these surgeries, from understanding the conditions that necessitate them, to the surgical process, potential risks, and the crucial recovery and rehabilitation phase.
Recap of Key Points
 Understanding the Need: Foot reconstruction surgery is a transformative option for those suffering from conditions like flat feet or Charcot foot, which can cause pain and mobility issues.
Understanding the Need: Foot reconstruction surgery is a transformative option for those suffering from conditions like flat feet or Charcot foot, which can cause pain and mobility issues.- The Surgical Journey: The process involves careful pre-surgical planning, the surgery itself, and a vigilant approach to post-operative care.
- Navigating Risks and Recovery: While there are risks associated with any surgical procedure, understanding and adhering to recovery protocols significantly enhances outcomes.
- The Role of Rehabilitation: Physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments are pivotal in regaining foot function and returning to daily activities.
Final Thoughts and Advice
If you or a loved one is considering foot reconstruction surgery, it’s essential to consult with a qualified foot and ankle surgeon who can provide personalized advice based on your specific condition. Remember, the journey to recovery requires patience and adherence to your healthcare provider’s guidance.
Continued Care and Support
Post-surgery, it’s important to maintain regular check-ups and follow a healthy lifestyle to ensure the longevity of the surgical outcomes. Stay active, wear appropriate footwear, and engage in exercises that maintain foot strength and flexibility.
Empowering Your Decision
We hope this guide has empowered you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about foot reconstruction surgery. Remember, this journey, though challenging, leads to a destination of improved mobility and a better quality of life.
Empowering Your Decision
We hope this guide has empowered you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about foot reconstruction surgery. Remember, this journey, though challenging, leads to a destination of improved mobility and a better quality of life.
FAQs
In this section, we address some of the most common questions about foot reconstruction surgery to help you better understand the process and what to expect.
What Conditions Necessitate Foot Reconstruction Surgery?
Foot reconstruction surgery is typically recommended for conditions that cause significant pain, deformity, and functional impairment. These include flat feet, Charcot foot, severe bunions, hammertoes, and injuries that have led to misalignment or loss of function.
How Long Does Recovery from Foot Reconstruction Surgery Take?
The recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and the individual’s overall health. Generally, it can range from several weeks to several months. Full recovery, where patients can return to all their normal activities, may take up to a year.
 Is Foot Reconstruction Surgery Painful?
Is Foot Reconstruction Surgery Painful?
Patients will experience some level of discomfort post-surgery, but pain management techniques, including medications, ice, and elevation, are used to control this. The level of pain typically decreases significantly within the first few weeks after surgery.
What Are the Risks Associated with Foot Reconstruction Surgery?
As with any surgery, there are risks such as infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and complications from anesthesia. However, these risks are generally low and can be further minimized by following your surgeon’s pre- and post-operative instructions.
Will I Need Physical Therapy After Surgery?
Yes, physical therapy is a crucial part of the recovery process. It helps in regaining strength, flexibility, and mobility in the foot and ankle.
Can Foot Reconstruction Surgery Correct My Condition Permanently?
While foot reconstruction surgery aims to permanently correct the condition, the outcome depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s adherence to post-operative care, and overall health. In some cases, further treatment or surgery may be required.
How Can I Ensure the Best Outcome from My Surgery?
Following your surgeon’s instructions closely, attending all follow-up appointments, engaging in prescribed physical therapy, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments are key to ensuring the best outcome.


 Understanding the Need: Foot reconstruction surgery is a transformative option for those suffering from conditions like flat feet or Charcot foot, which can cause pain and mobility issues.
Understanding the Need: Foot reconstruction surgery is a transformative option for those suffering from conditions like flat feet or Charcot foot, which can cause pain and mobility issues. Is Foot Reconstruction Surgery Painful?
Is Foot Reconstruction Surgery Painful?