Table of Contents
Introduction
Flat feet, or pes planus, are a common condition characterized by the absence of an arch in the foot. This leads to foot pain, as the sole makes complete or near-complete contact with the ground. Whether you’re experiencing discomfort or seeking preventive care, understanding your options, including non-surgical and flat feet surgery options, is crucial for maintaining foot health and quality of life.
Understanding Flat Foot Pain
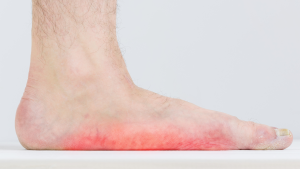 Flat feet, medically known as pes planus, manifest when the arch inside the foot flattens, allowing the sole to touch the ground fully or almost fully when standing. Recognizing pes planus symptoms early is key to seeking appropriate treatment. Consulting a podiatrist for flat feet is essential for a personalized diagnosis and exploring the best treatment paths. Options range from conservative management to flat foot orthotics and surgery for more severe cases of rigid pes planus.
Flat feet, medically known as pes planus, manifest when the arch inside the foot flattens, allowing the sole to touch the ground fully or almost fully when standing. Recognizing pes planus symptoms early is key to seeking appropriate treatment. Consulting a podiatrist for flat feet is essential for a personalized diagnosis and exploring the best treatment paths. Options range from conservative management to flat foot orthotics and surgery for more severe cases of rigid pes planus.
Anatomy of the Foot
The human foot is a complex structure composed of bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments that work together to provide support, balance, and mobility. The arch of the foot plays a crucial role in this system, functioning as a natural shock absorber. In individuals with flat feet, the arch’s inability to properly absorb impact can lead to a range of issues, from immediate discomfort to long-term musculoskeletal problems.
Flexible vs. Rigid Flat Foot
Flexible Flat Foot: This condition is often identified in childhood and can persist into adulthood. It’s typically painless and may not require treatment unless discomfort or secondary problems develop. The flexibility of the arch indicates that with proper support, the foot can function more effectively, reducing potential issues.
Rigid Flat Foot: Unlike its more flexible flatfoot counterpart, rigid flatfoot deformity of foot can result from congenital bone conditions, trauma, or diseases that affect the musculoskeletal or nervous system. It is more likely to be associated with pain and problems with foot function, necessitating a more proactive approach to management and treatment.
Understanding the type of flat foot and its underlying cause is essential for effective treatment. For individuals with flat feet, especially those experiencing discomfort or pain, a consultation with a foot doctor or podiatrist is crucial. These specialists can offer a comprehensive evaluation, diagnose the specific nature of the most flexible flat feet or foot condition, and recommend appropriate flat feet treatment options. In cases where conservative measures are insufficient, flat feet surgery may be discussed as a possible approach to alleviate symptoms and improve foot function.
Causes of Flat Foot
 Flat feet (pes planus) can arise from various causes, including genetic predisposition, developmental issues during childhood, and injuries. However, lifestyle choices also play a significant role in exacerbating or, in some cases, contributing to the development of flat feet. Understanding the interplay between these factors is crucial in identifying the most effective treatment approaches.
Flat feet (pes planus) can arise from various causes, including genetic predisposition, developmental issues during childhood, and injuries. However, lifestyle choices also play a significant role in exacerbating or, in some cases, contributing to the development of flat feet. Understanding the interplay between these factors is crucial in identifying the most effective treatment approaches.
Genetic Predisposition and Heredity:
Genetics remains a primary factor in the development of flat feet. A family history of the condition can significantly increase the likelihood of inheriting flat arches, underscoring the importance of early monitoring and intervention.
Developmental Issues During Childhood:
The arches of the feet typically develop through childhood and adolescence. In some cases, this development does not proceed as expected, leading to flat feet. Such instances highlight foot deformity and the need for attention to foot health from an early age.
Injury or Trauma:
Traumatic events to the foot or ankle, such as fractures and sprains, can damage the tendons and ligaments that support the arch, potentially leading to or exacerbating flat feet.
Conditions Affecting Muscles or Nerves:
Certain medical conditions that weaken the muscles or affect the nervous system can contribute to the collapse of the arch, illustrating the complex interconnections between overall health and foot structure
Aging, Obesity, and Other Risk Factors:
The natural aging process and obesity are also significant contributors. Aging can weaken the tendons and ligaments that support the foot’s arch, while obesity increases pressure on the foot, both leading to flat feet.
Environmental Influences:
Prolonged standing or walking, especially on hard surfaces and in unsupportive footwear, can be a risk factor for developing flat feet or exacerbating existing conditions.
Symptoms and Signs of Flat Foot
Identifying the symptoms and signs of flat feet (pes planus) is crucial for timely diagnosis and management. Dr. Wilder, a renowned podiatrist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating various foot conditions, emphasizes the importance of recognizing these early indicators to prevent further complications. According to Dr. Wilder, while some individuals with flat feet may not experience any discomfort, others might face a range of symptoms that can significantly impact their quality of life. The common symptoms and signs associated with flat feet include:
Common Symptoms
 The most commonly reported symptom of flat feet is pain, particularly concentrated in the heel or arch area of the foot. This discomfort often intensifies during physical activities and tends to subside with rest. Such pain signals the stress and strain placed on the foot due to the flattened arch, highlighting the importance of proper diagnosis and management.
The most commonly reported symptom of flat feet is pain, particularly concentrated in the heel or arch area of the foot. This discomfort often intensifies during physical activities and tends to subside with rest. Such pain signals the stress and strain placed on the foot due to the flattened arch, highlighting the importance of proper diagnosis and management.
Another key indicator of flat feet is the collapse of the arch, which becomes visibly flattened when the individual is standing. This condition may not be as noticeable when the person is sitting or lying down, particularly in cases of flexible flat foot. The visible change in the foot’s structure when bearing weight underscores the dynamic nature of this condition and the varying degrees of its manifestation.
Swelling along the inside of the ankle is also a common symptom, resulting from the additional stress on the foot’s ligaments and tendons. This swelling is a direct consequence of the altered biomechanics of the foot due to the flattened arch, leading to inflammation and discomfort in the affected area.
Lastly, individuals with flat feet may face difficulty in performing movements that require the foot to flex in specific ways, such as standing on tiptoe. This limitation reflects the impact of flat feet on the overall functionality and flexibility of the foot, affecting daily activities and mobility. Addressing these symptoms through appropriate medical intervention is crucial for improving quality of life and foot health.
Impact on Overall Posture and Alignment
Dr. Wilder also points out that flat feet can affect more than just the feet; they can lead to misalignment of the legs, which might impact overall posture. This misalignment can lead to discomfort causing pain in the knees, hips, and lower back due to the altered distribution of body weight.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Pes Planus (Flat Feet)
Consult a podiatrist for pes planus (flat feet) symptoms for a tailored treatment plan, as emphasized by Dr. Wilder, to prevent complications. Seek medical advice if experiencing persistent foot pain, noticeable foot structure changes, impact on daily activities, or additional symptoms like stiffness or reduced flexibility. Early intervention is crucial for effective management, involving physical examinations and possibly imaging tests to assess severity and treatment options. With proper care, including exercises, orthotics, or surgery for severe cases, individuals can significantly improve symptoms and foot health.
Diagnosis of Flat Foot: Enhanced Section with Differential Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of flat feet involves a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional, where the importance of differential diagnosis comes into play. Dr. Wilder, emphasizes the critical role of a thorough evaluation, which includes not only discussing symptoms and conducting imaging tests but also distinguishing flat feet from other foot conditions that may present similar symptoms.
Physical Examination and Patient History:
The described process for diagnosing and assessing flat feet encompasses a comprehensive approach, combining patient history, physical examination, gait analysis, and imaging tests. Each of these steps plays a crucial role in ensuring an accurate diagnosis and forming the basis for an effective treatment plan. Let’s break down each step:
Physical Examination and Patient History
The first step usually involves understanding the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. During the history-taking, the healthcare provider might ask about any pain, the presence of flat feet in the family, the duration of the symptoms, and if any activities exacerbate the condition. The physical examination focuses on the feet and ankles, assessing for any abnormalities, flexibility of the flat foot (rigid vs. flexible flatfoot), arch presence when the child is on tiptoes, and signs of any associated conditions.
Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is a critical step in diagnosing flat feet, as it helps in identifying any abnormalities in the walking pattern that flat feet might cause. During gait analysis, the healthcare provider observes the patient as they walk, looking for patterns such as overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot after landing), which is common in flat feet. This analysis can also help in determining the impact of flat feet on the patient’s posture and overall biomechanics.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests provide a more detailed view of the foot’s structure, helping to confirm the diagnosis and identify any underlying conditions or complications that might not be apparent from a physical exam alone. The choice of imaging test can depend on the specific circumstances:
- X-rays are typically the first line of imaging used. They can show the alignment of the foot bones and any abnormalities in the arch.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is more detailed and can provide images of the soft tissues, including muscles and ligaments. This is particularly useful if a tendon injury or other soft tissue abnormalities are suspected.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans offer detailed images of the bone structures and can be used to assess complex deformities.
By integrating these approaches, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose flat feet and understand the extent to which the condition affects the patient. This comprehensive assessment is vital for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual needs of the child, which might include physical therapy, orthotic devices, exercises, or, in severe cases, surgery.
The Role of Podiatrist:
Podiatrists play a crucial role beyond diagnosing flat feet, crafting personalized treatment plans that include conservative methods, orthotic device guidance, and possibly surgery. Their goal is to alleviate pain, improve foot function, and enhance quality of life. Specialized in differential diagnosis, they differentiate flat feet from similar conditions, ensuring treatments meet each patient’s unique needs. After thorough evaluations, they recommend suitable treatments, ranging from non-invasive to surgical options, aimed at optimal patient outcomes.

Living with Flat Foot
Living with flat feet (pes planus) can be challenging, However, with the right strategies and support, individuals can effectively manage their condition and lead active, comfortable lives. Dr. Wilder, a podiatrist specializing in foot and ankle conditions, offers valuable advice for those navigating the complexities of flat feet. Here are essential tips and insights for managing flat foot and maintaining optimal foot health:
Daily Management Tips
 Wear Supportive Footwear: Choosing shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole is crucial for people with flat feet. This can help distribute weight more evenly and reduce stress on the arches.
Wear Supportive Footwear: Choosing shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole is crucial for people with flat feet. This can help distribute weight more evenly and reduce stress on the arches.- Incorporate Orthotic Devices: Custom or over-the-counter orthotic devices designed to support the arch can make a significant difference in comfort and function. Dr. Wilder can advise on the best type of orthotic for your specific needs.
- Stay Active within Comfort Limits: Engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, or walking can help maintain fitness without putting excessive strain on the feet.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight can exacerbate the pressure on flat feet, leading to increased discomfort. A healthy diet and regular exercise can help manage weight and reduce foot strain.
Footwear Recommendations
Dr. Wilder emphasizes the importance of proper footwear for individuals with flat feet. Shoes that provide adequate arch support and have a firm heel counter are ideal. Avoid wearing shoes with high heels and shoes with minimal support, as these can worsen symptoms. In some cases, special footwear designed for flat feet may be recommended.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to wearing supportive footwear and using orthotic devices, making lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing severe pain from flat feet. This includes avoiding activities that exacerbate foot pain, practicing foot-strengthening exercises as recommended by a podiatrist, and taking breaks to rest and elevate the feet when necessary.
Flat Foot Reconstruction Surgery: A Comprehensive Solution
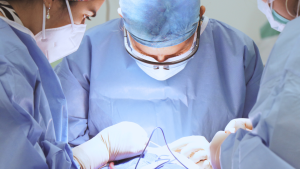 For individuals with severe pes planus who haven’t found relief through conservative treatments, flat foot reconstruction surgery presents a definitive solution. This surgical procedure aims to restore the natural arch of the foot, improve functionality, and alleviate pain. The process involves correcting the shape and alignment of the foot’s bones, repairing or replacing damaged ligaments, and sometimes using implants to support the arch. Recovery from flat foot reconstruction surgery requires time, physical therapy, and a tailored rehabilitation plan. Consulting with a specialized podiatrist, like Dr. Joshua Wilder, can help patients understand the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of this transformative procedure. For those suffering from debilitating flat foot conditions, reconstruction surgery offers a path to improved mobility and quality of life.
For individuals with severe pes planus who haven’t found relief through conservative treatments, flat foot reconstruction surgery presents a definitive solution. This surgical procedure aims to restore the natural arch of the foot, improve functionality, and alleviate pain. The process involves correcting the shape and alignment of the foot’s bones, repairing or replacing damaged ligaments, and sometimes using implants to support the arch. Recovery from flat foot reconstruction surgery requires time, physical therapy, and a tailored rehabilitation plan. Consulting with a specialized podiatrist, like Dr. Joshua Wilder, can help patients understand the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes of this transformative procedure. For those suffering from debilitating flat foot conditions, reconstruction surgery offers a path to improved mobility and quality of life.
Long-term Outlook and Monitoring
With proper management, individuals with flat feet often lead active lives without major restrictions, but ongoing monitoring is necessary as symptom or structure changes may demand treatment adjustments. Regular visits to a podiatrist are crucial for optimal foot health. Flat feet’s effects range from symptom-free to causing significant discomfort and mobility issues, making tailored treatments like orthotics, physical therapy, or surgery vital for improving quality of life. If experiencing symptoms, consulting a podiatrist for personalized care is essential to alleviate pain and enhance foot function, underscoring the importance of proactive foot health management for overall well-being and mobility
Frequently Asked Questions about Flat Feet
How Can Flat Feet Be Managed?
- Orthotic Devices: Prescribed by a podiatrist for arch support.
- Supportive Footwear: Shoes with arch support relieve discomfort.
- Surgery: For severe cases to correct issues.
How Do I Know If I Have Flat Feet?
- Visual Inspection: Flat arches when standing.
- Wet Foot Test: Full imprint on a flat surface indicates flat feet.
- Symptom Check: Pain and swelling may suggest flat feet.
What Causes Flat Feet?
- Genetics: Family history increases risk.
- Aging: Tendons weaken over time.
- Injury: Can lead to flat feet.
- Medical Conditions: Like muscular dystrophy.
- Pregnancy/Obesity: Extra stress on feet.
What Is Flat Foot?
A condition where the foot’s arch is lower than a normal arch or flat, causing the sole tip toe to fully or nearly fully touch the ground. It can be flexible (arch appears when not bearing weight) or rigid (arch is always flat).
Can Flat Feet Be “Fixed”?
While you can’t change the foot shape or structure completely, symptoms can be managed through orthotics, supportive shoes, therapy, or surgery in some cases. Consult a podiatrist for a personalized plan.
Understanding flat feet and how to manage them can lead to better foot health and an improved quality of life. If you suspect you have flat feet or experience any related discomfort, seeking advice from a podiatrist is the best course of action.
About Dr. Joshua Wilder
 Dr. Joshua Wilder, a skilled podiatrist based in Snellville, GA, brings a wealth of expertise and a compassionate care approach. With roots in Pittsburgh, PA, and an upbringing in Cincinnati, OH, Dr. Wilder’s medical journey led him through rigorous training in rearfoot reconstruction and limb salvage during his residency in Pittsburgh. He further specialized in pediatrics and forefoot reconstruction during a fellowship in Atlanta, GA, highlighting his comprehensive skill set in treating foot and ankle conditions across all age groups.
Dr. Joshua Wilder, a skilled podiatrist based in Snellville, GA, brings a wealth of expertise and a compassionate care approach. With roots in Pittsburgh, PA, and an upbringing in Cincinnati, OH, Dr. Wilder’s medical journey led him through rigorous training in rearfoot reconstruction and limb salvage during his residency in Pittsburgh. He further specialized in pediatrics and forefoot reconstruction during a fellowship in Atlanta, GA, highlighting his comprehensive skill set in treating foot and ankle conditions across all age groups.
Dr. Wilder is deeply committed to a patient-centered approach, emphasizing collaboration and empathy in patient care. He believes in creating a judgment-free, open doctor-patient relationship, treating patients like family to ensure the best medical outcomes.
Education & Professional Affiliations
- Undergraduate: Washington and Jefferson College, Pittsburgh, PA
- Medical School: Kent State University College of Podiatric Medicine, Cleveland, OH
- Residency: Western Pennsylvania Hospital, Pittsburgh, PA
- Fellowship: Emory St. Joseph Hospital, Atlanta, GA (Pediatric and Adult Reconstructive Foot and Ankle Surgery)
He is associated with the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons and a member of the American Podiatric Medical Association, Georgia Podiatric Medical Association, and Western Pennsylvania Foot and Ankle Society. These affiliations attest to his dedication to excellence in podiatric care.


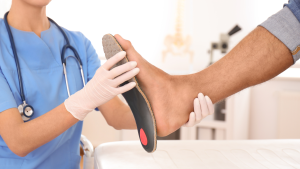 Wear Supportive Footwear: Choosing shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole is crucial for people with flat feet. This can help distribute weight more evenly and reduce stress on the arches.
Wear Supportive Footwear: Choosing shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole is crucial for people with flat feet. This can help distribute weight more evenly and reduce stress on the arches.


