Introduction
Diabetic ulcers present serious risks for those with diabetes. Often found on the legs, these sores can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Therefore, effective treatment is crucial to manage their progression or even prevent them.
In this guide, we explore the causes, symptoms, and comprehensive treatments for diabetic ulcers.
Table of Contents
Understanding Diabetic Ulcers
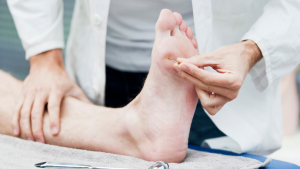 Diabetic ulcers on the leg are chronic sores that typically appear on the lower legs and feet of individuals with diabetes, similar to venous ulcers which also manifest as chronic leg sores. These ulcers stem from a combination of factors including poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Importantly, the impaired blood flow and reduced sensation contribute to the skin’s vulnerability, making even minor injuries potentially severe.
Diabetic ulcers on the leg are chronic sores that typically appear on the lower legs and feet of individuals with diabetes, similar to venous ulcers which also manifest as chronic leg sores. These ulcers stem from a combination of factors including poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Importantly, the impaired blood flow and reduced sensation contribute to the skin’s vulnerability, making even minor injuries potentially severe.
Firstly, recognizing the primary causes is crucial for prevention and early treatment. Diabetes often leads to neuropathy, where patients lose sensation in their feet. Consequently, they may not notice small wounds, which can develop into ulcers if untreated. Additionally, compromised immune responses in diabetic individuals mean these wounds heal slowly and can easily become infected, mirroring some venous ulcer symptoms.
Secondly, identifying the early signs of diabetic ulcers can significantly improve outcomes. Symptoms typically include swelling, discoloration, and the presence of drainage from a wound—common signs that are shared with venous ulcers. Promptly addressing these signs with medical intervention can prevent complications such as severe infections or, in extreme cases, amputation.
By understanding these aspects, individuals can better manage their health and prevent the progression of ulcers. Awareness and education are key in mitigating the risks associated with diabetic and venous ulcers
Symptoms and Early Detection
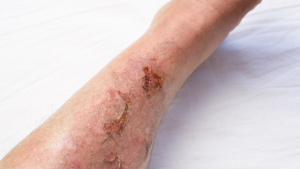 Early detection of diabetic leg ulcers , including venous ulcers, is crucial for preventing serious complications. Recognizing the symptoms, particularly venous ulcer symptoms, promptly can lead to timely and effective treatment. Here are the primary signs to watch for:
Early detection of diabetic leg ulcers , including venous ulcers, is crucial for preventing serious complications. Recognizing the symptoms, particularly venous ulcer symptoms, promptly can lead to timely and effective treatment. Here are the primary signs to watch for:
- Swelling: Often one of the first noticeable signs, swelling around a foot or lower leg can indicate the beginning stages of an ulcer.
- Discoloration: Look for skin color changes, especially areas that turn red, blue, or black. This discoloration often signifies poor circulation and is a precursor to skin breakdown.
- Drainage: Any drainage or oozing from an area on the foot suggests that an open wound may be present, even if it’s not visible immediately.
- Odor: An unusual odor emanating from a foot can be a sign of an infection related to a diabetic ulcer.
- Temperature Change: A foot becoming significantly warmer or cooler than usual can indicate underlying issues.
Furthermore, early detection involves more than observing symptoms—it requires proactive management. Individuals with diabetes should regularly inspect their feet using a mirror to check areas that are hard to see. Additionally, regular checkups with a healthcare provider are essential, as they can spot signs that might be missed at home.
Lastly, it’s crucial to educate patients and their families about these symptoms. Awareness and knowledge empower individuals to take action before minor issues escalate into major complications.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
Effective management of diabetic ulcers involves a multifaceted approach, ensuring treatments are tailored to individual needs. This section outlines the primary treatment strategies:
-
Medical Treatments:

- Wound Care Management: Regular cleaning and dressing changes are fundamental. Using appropriate dressings helps manage exudate and protects the ulcer from infection.
- Medications: Antibiotics are often prescribed to combat infection, while pain relievers help manage discomfort. Additionally, medications to improve blood flow can be crucial.
- Advanced Treatments: Techniques like hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be recommended to enhance healing by increasing oxygen supply to the wound.
-
Surgical Options:
- Debridement: This involves removing dead tissue from the ulcer, which is essential for promoting healing.
- Skin Grafts: For larger or deeper ulcers that do not heal with traditional methods, skin grafts may be necessary.
- Vascular Surgery: Improving blood flow through surgical interventions can significantly enhance healing rates for ulcers caused by poor circulation.
-
Lifestyle and Home Remedies:
- Dietary Changes: Maintaining a healthy diet helps control blood sugar levels, which is critical in wound healing.
- Blood Sugar Management: Regular monitoring and control of blood sugar are vital to prevent new ulcers and aid the healing of existing ones.
- Regular Foot Care: Daily inspection and care of feet can prevent complications. This includes moisturizing to prevent dry skin and avoiding walking barefoot.
Furthermore, Patients should understand their treatment plan and the importance of adherence to all medical advice.
Prevention Strategies
 Preventing diabetic ulcers is far more preferable than treating them. Effective prevention strategies can significantly reduce the risk of developing ulcers and facilitate better overall health management for individuals with diabetes. Here are key strategies to consider:
Preventing diabetic ulcers is far more preferable than treating them. Effective prevention strategies can significantly reduce the risk of developing ulcers and facilitate better overall health management for individuals with diabetes. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Daily Foot Care: Daily inspection of the feet is essential. Look for any signs of redness, blisters, cuts, or infections. Use a mirror to check all areas of the feet, especially those hard to see.
- Proper Footwear: Wear well-fitting, comfortable shoes that provide good support and cushioning. Avoid shoes that pinch or rub. Consider custom orthotic devices if recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep the skin on your feet moisturized to prevent dryness and cracking, but avoid applying lotion between the toes where moisture can lead to fungal infections.
- Control Blood Sugar Levels: Maintain your blood sugar within recommended levels through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adhering to medication regimens. Stable blood sugar levels help prevent nerve damage and poor circulation, which are precursors to ulcers.
- Stop Smoking: Smoking impairs circulation, significantly increasing the risk of foot ulcers. Quitting smoking can improve circulation and overall health.
- Regular Check-Ups: Visit your healthcare provider regularly for comprehensive foot exams. This is vital in catching potential problems before they develop into ulcers.
Additionally, educating yourself and others about the risks and prevention of diabetic ulcers can empower more people to take active steps in their health management. Awareness leads to action, and action leads to prevention.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetic Ulcers
What are diabetic ulcers?
Diabetic ulcers are open sores or wounds that typically occur on the feet or lower legs of people with diabetes. They are primarily caused by poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. Diabetic ulcers, like venous ulcers, can develop due to circulation issues, and recognizing early venous ulcer symptoms is vital for timely treatment.
Why are diabetic ulcers a concern?
If not properly managed, diabetic ulcers can lead to severe infections and complications, including the risk of amputation due to deep infection or extensive tissue damage. Venous ulcers, which share similar risk factors, can also result in serious complications if left untreated.
How can I tell if I have a diabetic ulcer?
Look for signs such as swelling, redness, warmth, and any drainage or unusual odors from the affected area. Venous ulcer symptoms, such as skin discoloration or tightness, can also indicate circulation problems. These symptoms, especially if persistent, should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
What should I do if I think I have a diabetic ulcer?
Immediately consult your healthcare provider for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve healing outcomes, whether it’s a diabetic ulcer or venous ulcer.
Can diabetic ulcers be prevented?
Yes, with diligent foot care, proper diabetes management, and regular check-ups, the risk of developing diabetic ulcers can be significantly reduced. Similar strategies can help prevent venous ulcers, particularly managing venous insufficiency. Daily inspection of the feet, wearing appropriate footwear, and controlling blood sugar levels are key preventive measures.
Are there lifestyle changes that help with diabetic ulcer management?
Absolutely. Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking can greatly influence the healing process and overall health. Additionally, ensuring proper foot hygiene and moisture control is crucial. Similar lifestyle changes can help prevent venous ulcers and improve venous health.



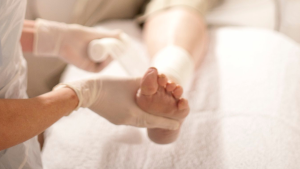
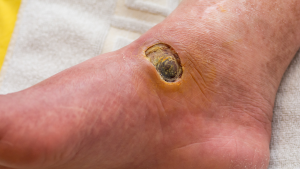 Managing diabetic ulcers, including venous ulcers, requires comprehensive care, often guided by a podiatrist. This care combines effective medical treatments with proactive preventive measures. The impact of diabetic and venous ulcers can be significant, but with diligent management under expert care, complications can be minimized or even prevented. We’ve explored various aspects of ulcer care—from understanding the condition and recognizing its symptoms, including venous ulcer symptoms, to exploring advanced treatments and everyday preventive strategies.
Managing diabetic ulcers, including venous ulcers, requires comprehensive care, often guided by a podiatrist. This care combines effective medical treatments with proactive preventive measures. The impact of diabetic and venous ulcers can be significant, but with diligent management under expert care, complications can be minimized or even prevented. We’ve explored various aspects of ulcer care—from understanding the condition and recognizing its symptoms, including venous ulcer symptoms, to exploring advanced treatments and everyday preventive strategies.



